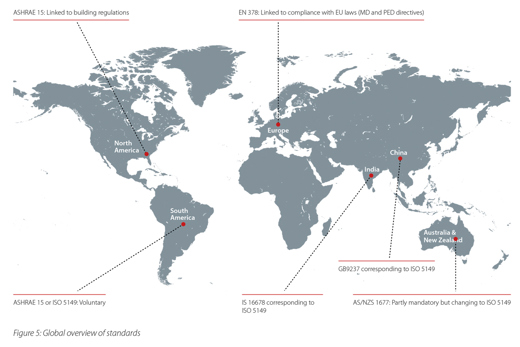
Specific guidance measures on market development—like GWP limits for certain applications—generate often challenges for market readiness and applicable safety standards. When new regulations are made, they are intended to encompass and balance the guidance measures and industry concerns.
HCFCs—particularly R22—are already phased out in all nondeveloping countries. Developing countries began phasing out HCFCs in 2015 and will continue until 2030. It is important to notice that the HCFC R22 can be used in many different applications, which makes the phase-out a challenge as no single non-flammable low-GWP refrigerant can replace it.
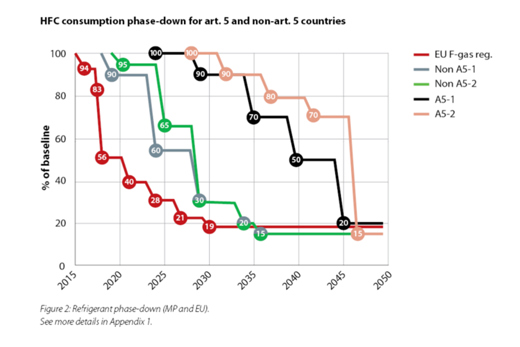
HFC consumption phase-down and Montreal protocol
In October 2016, the HFC phase-down steps were agreed and became part of the Montreal Protocol, also called the Kigali Amendment – which came into force on January 1st 2019. If ratified by a country after that date, the Kigali Amendment will enter into effect in the country 90 days afterwards. There is a special activity aimed at improving energy efficiency while phasing down HFCs called the Kigali Cooling Efficiency Program (KCEP). The KCEP is expected to spur the introduction of sustainable technologies in the fast-growing cooling segment.

Legislative frame and industry solutions
Besides the phase-down and phase-out mechanisms discussed above, many governments are applying measures for reducing high-GWP refrigerant consumption, such as GWP-weighted taxes. To date, Spain, Denmark, Norway and Sweden have imposed taxes on HFCs. Additionally, national incentives in the form of subsidies on low-GWP refrigerants are currently being used in many other countries.


External resources
Read further more via the external link below