Use of district heating equals higher individual comfort and energy efficiency
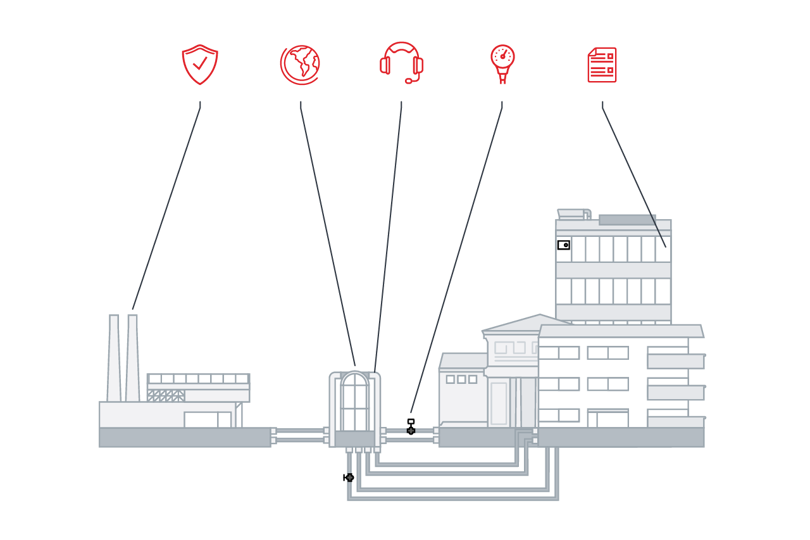
The basic principles behind district energy are remarkably simple. At one end of the network is an energy source (often a multi-fuel CHP plant). Heat is then distributed via a network of insulated pipes to residential, commercial and industrial buildings across the city.
At the end-user level, individual buildings are connected to the district heating network. In the building a substation with heat exchangers and various control components efficiently transfer hot water for room heating and domestic hot water (DHW) purposes into a building’s HVAC and DHW systems.
Choosing the right heat distribution system for a building (or network) is influenced by three main criteria:
- technical connection specifications;
- heat requirements of the building;
- comfort preferences of the building’s occupants.
The more accurately you can balance those needs, the better the service you will provide to your end-users and the more energy efficiency you will achieve. Both of these factors are good for your business.

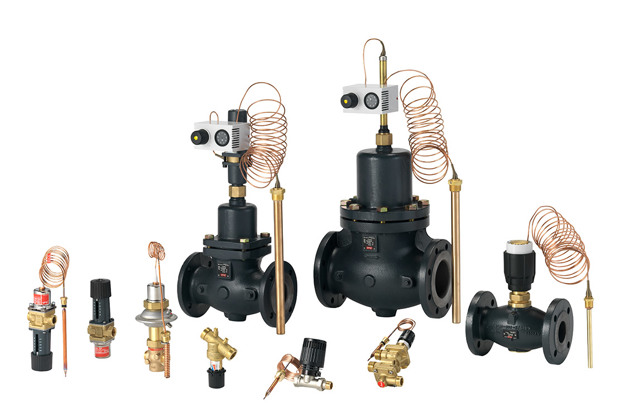
At Danfoss, we develop and produce all major components for our substations and flat stations in-house. Because we manufacture the key components ourselves, you will benefit from optimized heat transfer and system control performance. Pressure, differential pressure, temperature and flow are integrated and automatically controlled on nearly all Danfoss substations.
Controllers without auxiliary power, electronic controllers, motorized control valves and energy meters ensure maximum comfort and energy efficiency. They also enable integration into higher-level control and monitoring systems.
How we can help you
Wide product portfolio from flat stations to large site-specific heat transfer units and extensive range of control components
Consultancy and customer dedication, years of experience in buildings and maintaining district energy network
Innovation, technical optimization and performance
Safety and reliability in cooperation, expertise through the entire delivery chain of district energy
Global reach with strong local representation and know-how
Experience with all types of initial energy sources
Related products
-
if (isSmallPicture) {


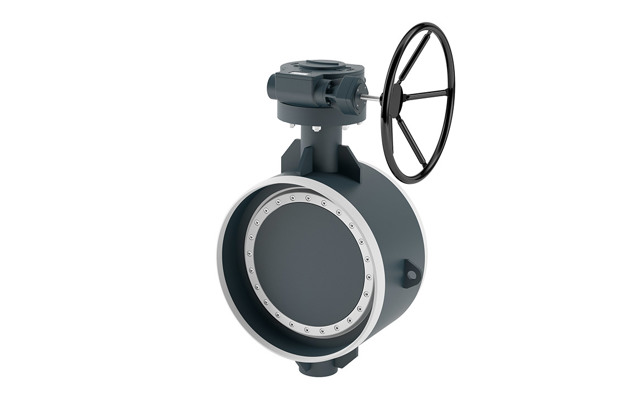
 Butterfly valves
Butterfly valvesButterfly valves are the components that provide on/off regulation of the district heating, HVAC or water applications where limited space is available for components.
-
if (isSmallPicture) {


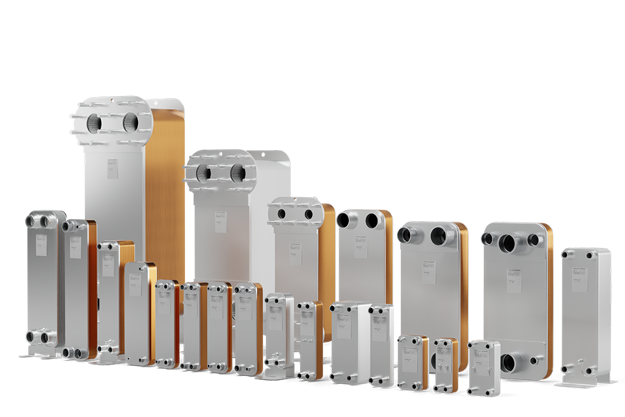
 Brazed heat exchangers
Brazed heat exchangersThe performance and efficiency of the Brazed Plate Heat Exchanger (BPHE) have been proven through 30 years of constant development to ensuring high efficiency
-
if (isSmallPicture) {


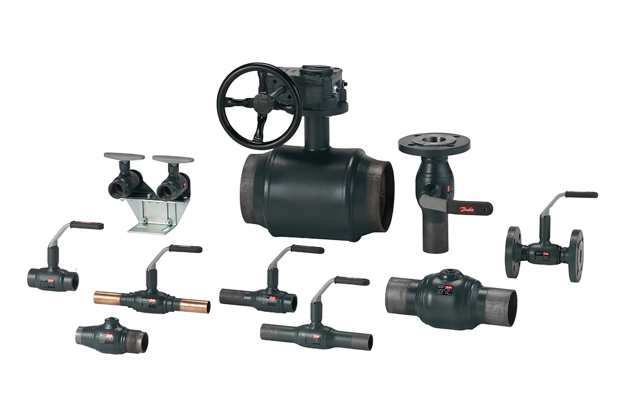
 Ball valves
Ball valvesBall valves enable on/off control of the building system connection. They create the sectioning of the system that enables service, maintenance and repairs to be carried out in sections, without shutting down or emptying the whole system.
-
if (isSmallPicture) {


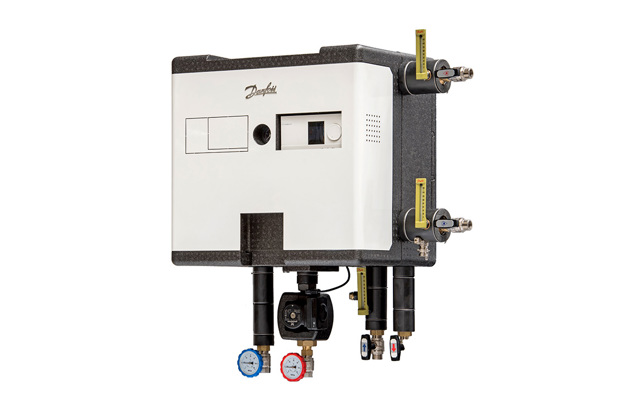
 Substations
SubstationsSubstations are house heating systems or units in apartments that handle heat transfer from district heating pipes into your home to get hot water and heat on demand.
-
if (isSmallPicture) {


 Self-acting temperature controllers
Self-acting temperature controllersThermostatic temperature controllers are used to control the flow temperature in instantaneous/storage domestic hot water and heating systems. In multi-family houses and commercial buildings, they are used for hot water systems and for return temperature limitation in district heating applications.
Tools and apps
Case studies
-
if (isSmallPicture) {


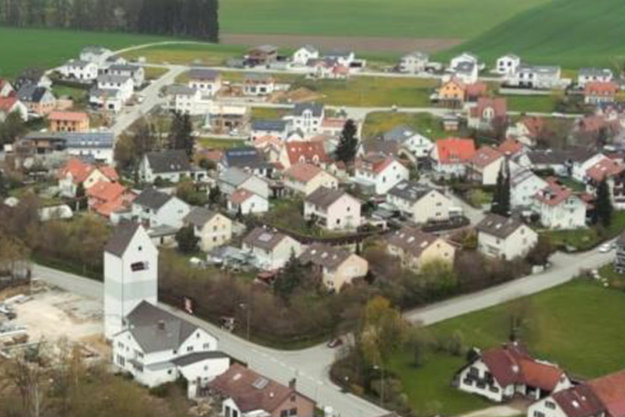
 Successful transition from oil boilers to a local heating network in Eurasburg
Successful transition from oil boilers to a local heating network in EurasburgIn the Wittelsbacher Land near Augsburg the local network in Eurasburg supplies heat to 80 buildings using a wood chip heating system. Danfoss’ substations ensure efficient heating in all building types, and its modern SCADA solution enables remote system monitoring and management.
-
if (isSmallPicture) {


 A cost-effective solution: district cooling in central Copenhagen
A cost-effective solution: district cooling in central CopenhagenEnergy efficiency was a major consideration in the design of Copenhagen’s district cooling project, where VLT® drives contribute to reducing CO2 emissions by more than 3000 t annually.
-
if (isSmallPicture) {


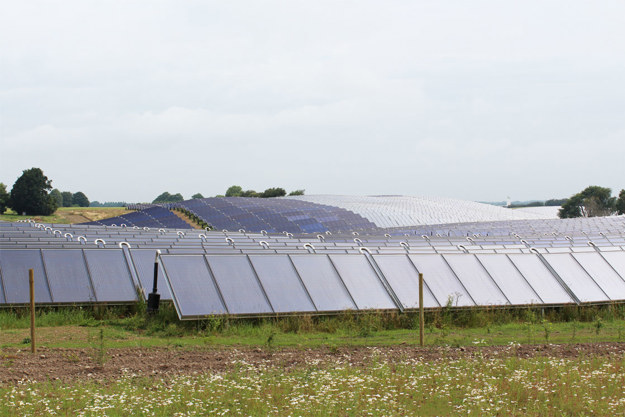
 Solar heating plant reduces CO2 emissions by 15,700 tonnes annually
Solar heating plant reduces CO2 emissions by 15,700 tonnes annuallyThe world’s largest solar heating plant in Silkeborg, Denmark harnesses energy to heat the homes and workplaces of 40,000 citizens. It supplies 18-20% of the annual heat consumption in the city of Silkeborg, Denmark, which has an ambitious target of CO2 neutrality in heat production by the year 2030.


























